Fiber optic cables are used to transmit data over long distances. They are made up of a core and a cladding. The core is made of a material that allows light to travel through it, and the cladding is made of a material that reflects light back into the core. This allows the light to travel through the cable without being lost.
There are two main types of fiber optic cables: multimode and single-mode. Multimode cables have a larger core than single-mode cables. This allows multiple light beams to travel through the cable at the same time. Single-mode cables have a smaller core, which allows only one light beam to travel through the cable at a time.
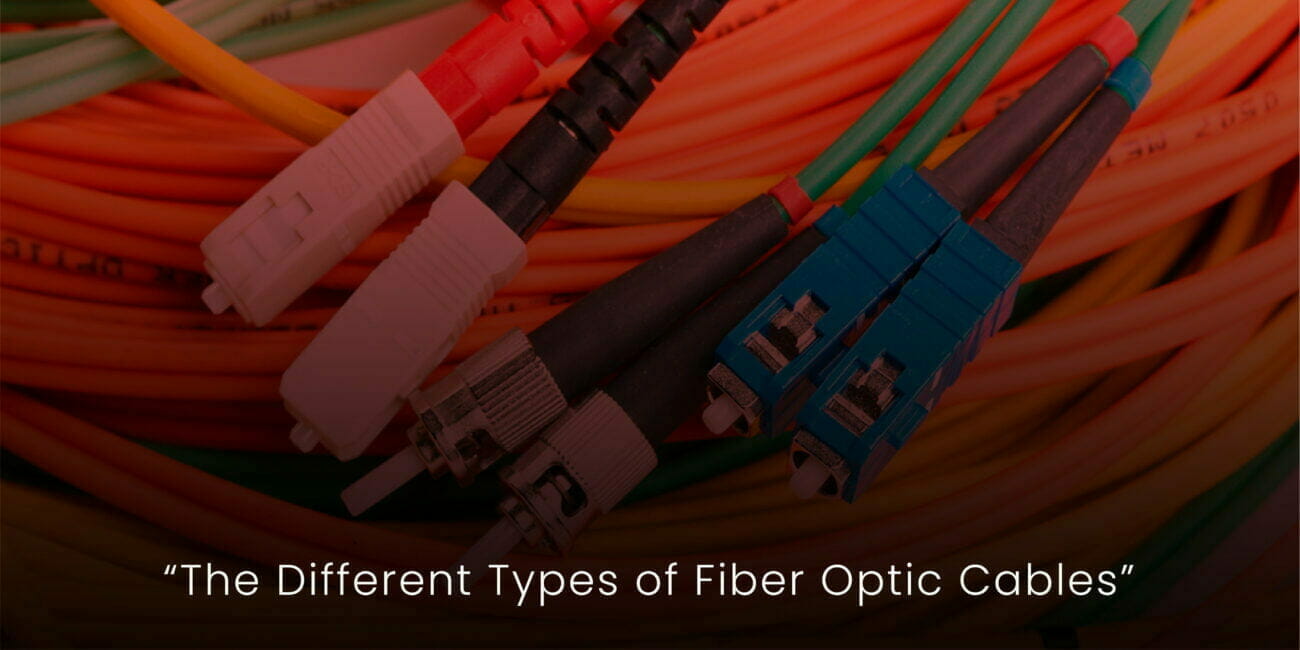
There are also two main types of fiber optic cable connectors: ST and SC. ST connectors are the older type of connector. They are larger and more difficult to connect than SC connectors. SC connectors are the newer type of connector. They are smaller and easier to connect than ST connectors.
The following table summarizes the different types of fiber optic cables:
| Type | Core Diameter | Cladding Diameter | Wavelength | Applications |
| Multimode | 50/62.5 micrometers | 125 micrometers | 850 or 1300 nanometers | Short distances, such as within a building |
| Single-mode | 9 micrometers | 125 micrometers | 1310 or 1550 nanometers | Long distances, such as between buildings or across cities |
Fiber optic cables are a versatile and reliable way to transmit data over long distances.
some additional details about the different types of fiber optic cables:
- Multimode fiber optic cables are the most common type of fiber optic cable. Multimode fiber optic cables are available in two different core diameters: 50/62.5 micrometers and 62.5/125 micrometers. The core diameter determines the maximum bandwidth of the cable. A 50/62.5 micrometer multimode fiber optic cable can support a bandwidth of up to 622 Mbps, while a 62.5/125 micrometer multimode fiber optic cable can support a bandwidth of up to 1 Gbps. Single-mode fiber optic cables have a much smaller core diameter than multimode fiber optic cables (9 micrometers versus 50/62.5 micrometers or 62.5/125 micrometers). This smaller core diameter allows only one light beam to travel through the cable at a time, which results in less signal attenuation and higher bandwidth.
Here are some of the advantages of using fiber optic cables:
- Fiber optic cables are capable of transmitting data over long distances without loss of signal strength.
- Fiber optic cables are immune to electromagnetic interference.
- Fiber optic cables are lightweight and easy to install.
- Fiber optic cables are a more secure way to transmit data than copper cables.
Here are some of the disadvantages of using fiber optic cables:
- Fiber optic cables are more expensive than copper cables.
- Fiber optic cables can be more difficult to terminate than copper cables.
- Fiber optic cables can be more susceptible to damage from physical stress.
Overall, fiber optic cables offer a number of advantages over copper cables. They are capable of transmitting data over long distances without loss of signal strength, they are immune to electromagnetic interference, and they are a more secure way to transmit data. However, fiber optic cables are more expensive than copper cables and can be more difficult to terminate.





